
About the author: NIKOLAY KHORKOV, founder and CEO of the Fibertool group of companies, is a successful entrepreneur and business development specialist with over 20 years of demonstrated expertise. MBA in Strategy and Finance with a proven track record in entrepreneurship, general management, and operations. Multiple successful ventures over the past two decades. Extensive C-level management experience with a focus on strategy and business development. Hardware and software engineering for fiber optic solutions.
Sustainability is a crucial objective that society endeavors to achieve. It encompasses the capacity of individuals to inhabit the Earth for extended periods while conserving its resources for future generations. In pursuit of a brighter future, the United Nations General Assembly has established a framework of 17 interconnected goals that address the most urgent environmental, economic, and social challenges. The efforts to tackle environmental issues have led to the evolution of the sustainable development concept. Over the past five decades, numerous strategies aimed at preserving natural resources and ecosystems, which are vital to life on Earth, have been actively deliberated.
Green Business Projects Overview
An increasing number of organizations worldwide are engaging in ESG transformations. According to NAVEX Global, a software company, 88% of public and over 60% of private companies globally have implemented sustainable development initiatives. These companies utilize renewable energy sources, reuse or recycle materials in their operations, collaborate with public associations, and prioritize customers and partners interested in adopting sustainability initiatives. Investment levels in such projects and production process improvements vary by organization size and industry. However, the Carbon Disclosure Project estimated that the world's 250 largest companies invested $3.9 trillion in sustainable development projects in 2020.
Businesses place particular emphasis on the environmental aspect, with carbon footprint reduction being the most ambitious objective. A study by consulting firm Accenture, which analyzed the reports of the 2,000 largest companies by revenue, revealed that nearly one-third of them aim to achieve net-zero emissions by 2050.
In 2022, most of these companies were in the following sectors:
Transport - 55% (+26% by 2021);
Financial markets - 54% (+5% by 2021);
Banking - 46% (+0% by 2021);
Housing and communal services - 43% (+8% by 2021);
Communications and media - 42% (+5% by 2021).
Telecommunications currently accounts for 8-10% of global energy consumption and 2-4% of greenhouse gas emissions, according to the European Commission. Recognizing the environmental risks, companies involved in constructing and operating telecommunications networks have started collaborating to implement green initiatives. This collaboration led to the formation of the European Green Digital Coalition (EGDC) in 2021, which now comprises 36 CEOs. Among its members are Microsoft, Nokia, IBM, Ericsson, Google, and Cisco. EGDC's primary objective is to maximize digitalization benefits to achieve sustainable development goals, meaning these companies not only work to reduce their own greenhouse gas emissions but also support the green digital transformation of sectors like energy, transport, agriculture, and construction with their solutions.
Although telecommunications company leaders have become more aware of sustainable development's importance, they have not always been successful in executing their projects. According to BCG's "Telco Sustainability Index" research, changes in their operations can hardly be considered significant yet. Concurrently, atmospheric emissions are projected to increase by 7% annually.
How did the performance of companies in different regions change in 2020-2021 (according to BCG)
Index | Europe | USA | Asia |
Total energy consumption (% change) | -22 | -5 | +4 |
Share of renewable energy in 2021 (and % change by 2020) | 72% (+19%) | 2% (+59%) | 1% (-17%) |
Total Waste (%) | +1% | -24% | -28% |
Share of waste recycled in 2021 (and % change by 2020) | 81% (+14%) | 54% (+12%) | 58% (+2%) |
The Role of Fiber Optics
One of the measures that help telecommunications companies reduce their environmental impact is the transition to fiber optics. This technology offers numerous advantages compared to copper cables, which are still widely used in network construction:
Reducing copper production: The mining industry currently accounts for approximately 8% of the global carbon footprint. According to Corning Inc., producing a 200-foot copper cable requires 2 kg of copper, and around 1,000 kg of hazardous substances are released into the atmosphere during mining. In contrast, the environmental impact of constructing a 200-foot optical fiber is estimated to be only 0.06 kg.
Lower equipment requirements: Fiber-optic communication lines require less equipment than copper due to the use of light for data transmission rather than electrical signals. Light signals can travel long distances along fibers with minimal power loss, leading to fewer signal amplifiers and reduced material usage.
Increased reliability and durability: Fiber optic cables, made of glass or plastic threads, are more reliable and durable than their copper counterparts. They are resistant to corrosion, temperature fluctuations, and electromagnetic interference, which means networks built using fiber optics are less likely to require repairs.
According to American Consumer, widespread adoption of fiber-optic internet could result in over 1 billion tons of greenhouse gas emissions reduction within a decade.
Notably, fiber optics not only directly contribute to sustainable development goals, but also indirectly aid companies and organizations in achieving them. For example, fiber optic networks are essential for the development of smart home and city technologies. A reliable, high-speed internet connection ensures the operation of devices that save and efficiently use resources, such as water, electricity, and fuel. Fiber optic sensors are also utilized for air quality monitoring.
Another benefit relates to the growing trend of remote work and the provision of remote services. Fiber-optic technologies are increasingly accessible to individuals, enabling them to access high-speed internet anywhere globally. This connectivity allows people to participate in business meetings, hold consultations or presentations, analyze data, and prepare reports without physical transportation. Consequently, the demand for transportation and large office spaces diminishes, reducing the environmental impact.
The Rising Popularity of Fiber Optics
The environmental benefits and efficiency of fiber optics are contributing to its increasing popularity each year. According to Statista, there were approximately 310 million fiber internet subscribers worldwide in 2016, which increased to 468 million by 2020. It is projected that by the end of 2023, there will be over 600 million global subscribers utilizing fiber-optic internet.
In the past year, among the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) member countries, the largest increase in fiber optic internet subscribers was recorded in Belgium (86.9%), Costa Rica (50.7%), the UK (46.6%), Ireland (39.6%), Chile (34.8%), Italy (34.3%), Colombia (31.7%), and France (31%).
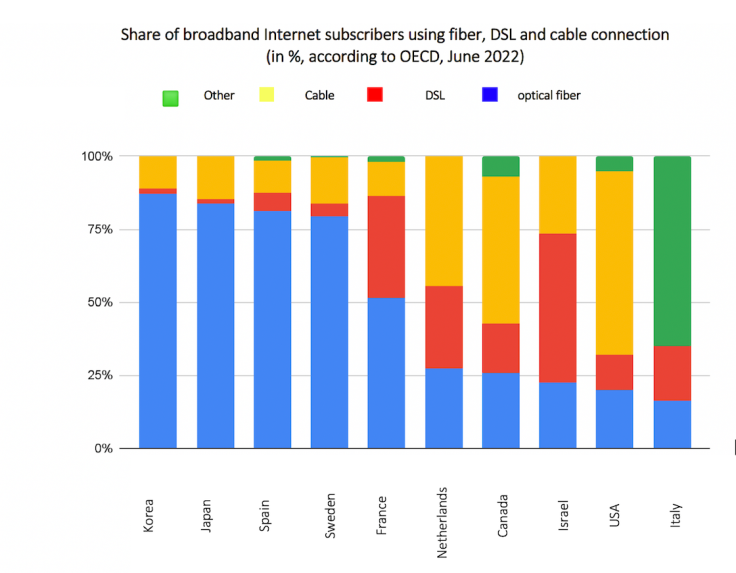
Simultaneously, among the OECD member countries, the highest percentage of subscribers connected to high-speed internet via fiber can be found in Korea (87.3%) and Japan (83.9%), where major fiber manufacturers are concentrated. In the United States, the majority of internet users are still connected through copper cables, with only 19.9% of subscribers using fiber optics. The lack of necessary infrastructure, particularly in rural areas, is cited as a primary reason for this lag.
The use of fiber optics not only contributes to addressing environmental issues but also assists in achieving other sustainable development goals. For example, it enables a large number of people to promptly consult medical professionals, access education, and find jobs to apply their acquired knowledge in practice. Fiber optics allows individuals previously excluded from digitalization benefits to fully participate in the global economy, improve their living standards, and contribute to worldwide prosperity.
As the demand for sustainable development grows, telecommunications sector companies must incorporate this focus into their daily operations and strategic planning. To achieve sustainable development goals, telecom executives must consistently monitor such projects and encourage their customers to follow a similar path.









