Over 100,000 flights take off and land every day globally, carrying around ~6M people. Ever wondered how they are organized efficiently, ensuring the safety of 0.1% of the population? Aircraft communication plays a pivotal role in maintaining orderly aviation operations. From takeoff to landing and during cruise, continuous and reliable communication between aircraft, ground stations, and other airborne entities is essential for coordinated and harmonious flight operations. This article explores the intricate landscape of aircraft communication, highlighting the critical role of broadcast antennas in facilitating seamless air traffic control (ATC) interactions throughout three flight phases.
1. Takeoff and Departure Phases
Ground-to-air communication is used to prepare aircraft for departure. Ground controllers utilize broadcast antennas to communicate essential information to pilots, such as taxi instructions, departure clearances, and initial flight paths. VHF (Very High Frequency) communication is predominantly used during this phase, operating within the 118.000 MHz to 136.975 MHz frequency range. Broadcast antennas at control towers and ground stations transmit VHF radio signals to aircraft, ensuring pilots are well-informed and guided as they navigate the airport environment.
2. Cruise Phase
During the cruise phase, aircraft rely on air-to-air communication to exchange position reports, traffic advisories, and other pertinent information with neighboring aircraft. Broadcast antennas onboard each aircraft transmit and receive VHF radio signals, enabling pilots to maintain situational awareness and coordinate their flight paths to ensure safe separation and efficient traffic flow. The use of broadcast antennas facilitates clear and concise communication between aircraft, fostering a collaborative and cooperative airborne environment.
For aircraft operating beyond the line-of-sight (BLOS) of traditional VHF communication, in other words, they cannot communicate with ground ATC, so satellite communication (SATCOM) systems come into play. Broadcast antennas equipped with SATCOM capabilities establish satellite links to exchange text messages, data, and voice communications with ATC and other aircraft worldwide. SATCOM systems provide global coverage and enhance communication resilience, ensuring continuous connectivity and effective coordination during oceanic, remote, and international flights.
3. Arrival and Landing Phase
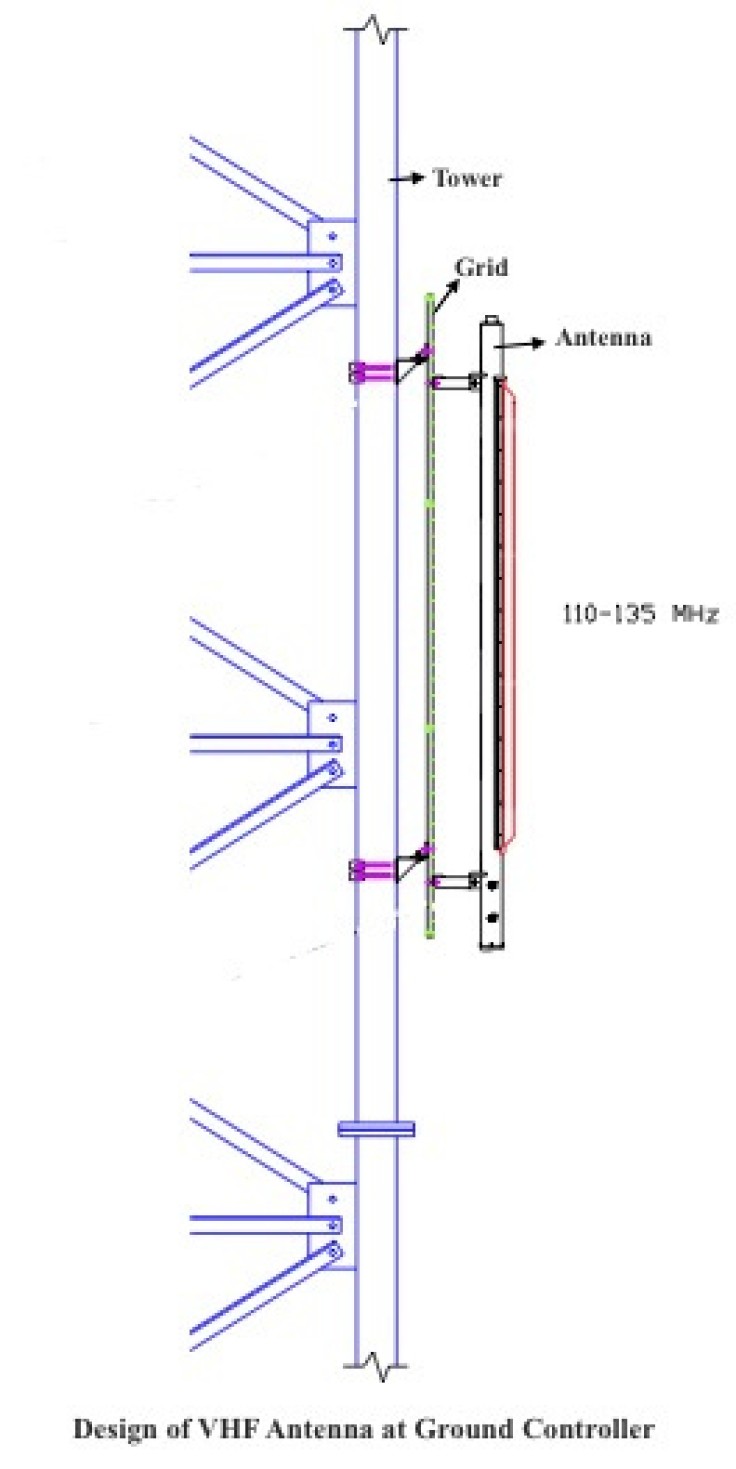
As aircraft approach their destination airports, pilots utilize broadcast antennas to communicate with ATC controllers, receiving landing clearances, approach instructions, and runway assignments. VHF communication remains the primary communication medium for air-to-ground interactions during this phase, with broadcast antennas at control towers and ground stations guiding aircraft safely to their final approach and landing.
In addition to communication, broadcast antennas integrated with radar systems play a crucial role in the landing phase, providing controllers with real-time surveillance data on aircraft positions, altitudes, and velocities. Radar antennas track aircraft movements, while broadcast antennas handle the communication aspect, ensuring seamless coordination between controllers and pilots to facilitate smooth landings and ground operations.
In conclusion, aircraft communication is essential for the smooth and safe functioning of aviation operations, managing the operations of over 100,000 daily flights and supporting the travel of approximately 6 million passengers globally. From the preparations for takeoff to the coordination during the cruise and the execution of the landing, continuous communication facilitated by broadcast antennas is crucial. Ground-to-air, air-to-air, and satellite communication systems, each using specific broadcast antennas, collaborate to keep pilots, ground controllers, and other aircraft informed throughout all flight phases. These communication systems guide aircraft through airports and enable interactions over oceanic areas and remote regions, overcoming line-of-sight limitations. Additionally, the integration of broadcast antennas with radar systems improves surveillance, providing controllers with real-time data for decision-making and safe landings. In summary, aircraft communication, supported by broadcast antennas, demonstrates the collaborative efforts and technological advancements in the aviation industry, contributing to the safety and efficiency of air travel for millions of passengers daily.









